Knee pain is a common problem of patients in all age groups. It can arise due to Knee Joint itself or conditions affecting the soft tissues in vicinity – ligaments, bursae and muscles that surround the knee. It can be caused by a sports injury, arthritis, work related injury or gradual wear and tear. Some signs and symptoms of knee pain include swelling and stiffness, redness and warmth, weakness, popping or crunching sounds or locking of the knee in the affected area. The impact of pain can be severe and widespread if overlooked. Contrary to a popular belief, most of the cases of knee pain are resolved with conservative management. At SAAOL Ortho Care, we offer a wide plethora of conservative and non-surgical treatment options for knee pain ranging from Lifestyle Modifications, exercises, electrical modalities, medications, weight management, nutrition and minimally invasive interventions which will help you to live life pain and disability free.
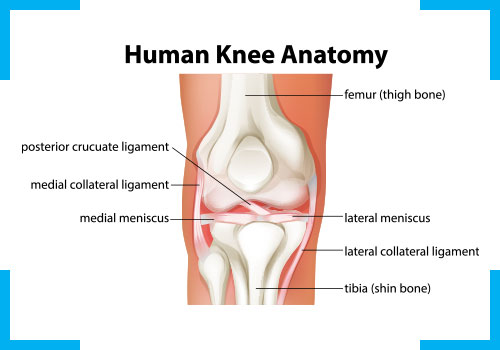
It is the largest and most complex synovial joints in the body of hinge variety. Responsible for weight bearing and propulsion, knee joint is made of Medial Tibio-Femoral, Lateral Tibio-Femoral and Patello-Femoral joints. It is surrounded by a number of tendons, ligaments and bursae. Quadriceps tendon connects the thigh muscles to patella (knee cap) while patellar tendon connects the patella onto the tibia. Ligaments are structures that connect bones to bones and provide stability to the joint. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) prevents the femur from sliding backward on the tibia (or the tibia sliding forward on the femur) while posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) prevents the femur from sliding forward on the tibia (or the tibia from sliding backward on the femur). The medial and lateral collateral ligaments prevent the femur from sliding side to side. Two C-shaped pieces of cartilage called the medial and lateral menisci act as shock absorbers between the femur and tibia. Knee is surrounded by numerous bursae, which are fluid filled spaces and help in smooth movement of the knee.
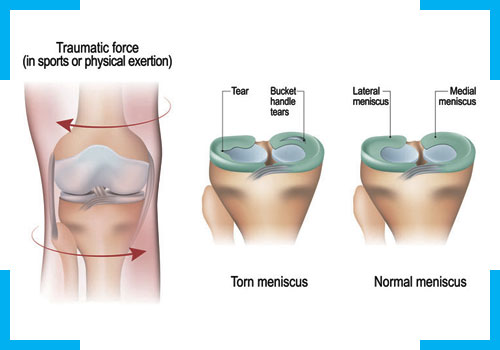
Menisici are 2 c-shaped cartilage in the knee that acts like a shock absorber between femur and tibia. Any activity that forcibly twists or rotates your knee can lead to tear of meniscus. Symptoms involve a popping sensation in the knee, swelling, stiffness, pain, feeling of give way of knee and difficulty in straightening. Treatment involves medications, ice, exercises, PEMF, UST, IFT, manual therapy, bracing, taping and PRP Injections.
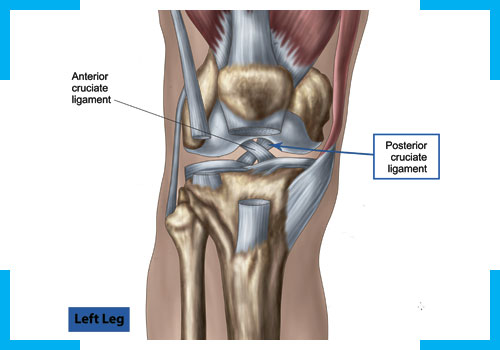
Cruciate ligaments are cross shaped proteinaceous structures that connect thighbone to shin bone and prevent their relative translation and thus providing stability. ACL injuries most commonly occur during sports that involve sudden stops or changes in direction, jumping and landing. Characterized by pain, swelling, redness, popping sensation, feeling of give way and instability, ACL/PCL tears can be managed conservatively using medications, rehabilitation, braces and PRP injections.
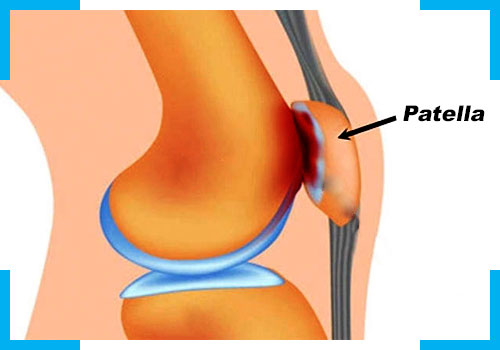
It is an important cause of anterior knee pain in young individuals that involves pain and discomfort around the knee cap. It can be caused due to overuse (in athletes), malalignment, muscular imbalances, increased Q-angle, chondromalacia patellae etc. Treatment involves medications, exercises, manual therapy, electrotherapy, kinesiotaping, PRP injections and viscosupplementation.
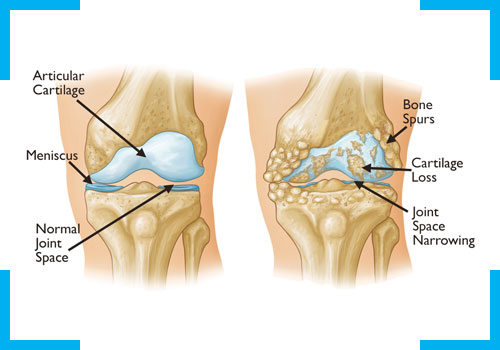
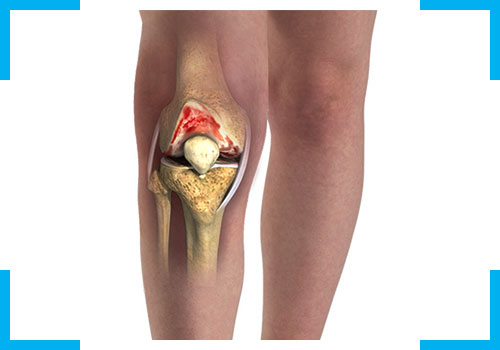
It is the most common form of arthritis which affects the knee most frequently. OA is caused due to degeneration or wear and tear of articular cartilage. When this happens, the bones in your knee joint rub together, causing friction that makes your knees hurt, become stiff or swell. OA in knees can occur in 50-60% individuals after 60 years of age. The common causes of wear and tear include age, female gender, genetics, obesity, metabolic issues like Diabetes, hypertension, flat feet, knee overuse or underuse, knee injury, other arthritis etc. This damage to cartilage can in turn lead to weakness of quadriceps that further causes knee deformity (Varus deformity). Knee OA is diagnosed using standing X rays of knee and graded using Kellgren-Lawrence staging. Non-surgical and holistic treatment involves medications, exercises, manual therapy, electrotherapy, weight reduction, customized insoles, diet, cartilage regeneration therapies, SAAOL Traction therapy and specialized injections like PRP, Viscosupplementation and Radiofrequency Ablation of Genicular Nerves.
– Knee joint can be affected by a number of other inflammatory and infective arthritis such as Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Reactive Arthritis, Septic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Post-Viral Arthritis etc. Pain, swelling, redness, warmth, stiffness and functional abnormalities are commonly seen in all these types. These arthritis can be managed without surgery using multimodal and holistic approach. Medications, rehabilitation, exercises, diet and interventional pain procedures are very helpful.
- The subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (SASD) is a potentially pain-sensitive structure of the glenohumeral joint. Located beneath acromion bone and deltoid muscle, inflammation in this empty space can be due to trauma, degeneration, systemic illness or overuse and can lead to impingement of supraspinatus muscle. When inflamed, a bursitis limits movements such as internal rotation, abduction and flexion. A dynamic ultrasound of shoulder can reveal bursitis and treatment is 100% non-surgical and holistic which includes medicines, electrotherapy, lifestyle modifications, exercises, diet and injections.
Knee bursitis can arise from inflammation of any bursa in the region of the knee joint and is a common clinical disorder that may lead to functional difficulties. In the popliteal fossa, a bursa is located between the medial head of the gastrocnemius and semimembranosus tendon. Swelling in this area is also called Baker’s cyst. Besides prepatellar, infrapatellar, suprapatellar and anserine bursitis can cause pain around the knee joint. All bursitis can be managed holistically using medications, exercises, electrical modalities, diet and injections.
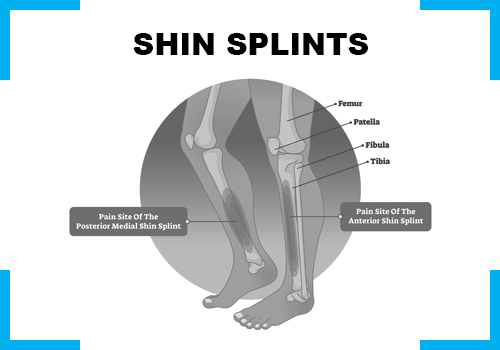
Also called Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome, it is defined in terms of pain and discomfort in the anterior portion of the leg from repetitive activity on hard surfaces or forcible, excessive use of the foot flexors. Shin splints most commonly occur in athletes who have sudden increases or changes in their training activity. Patients presenting with shin splints usually complain of a dull and aching pain near the junction of the mid and distal thirds of the posteromedial or anterior tibia. Treatment involves medications, customized foot insoles, exercises, modalities and pain management injections.